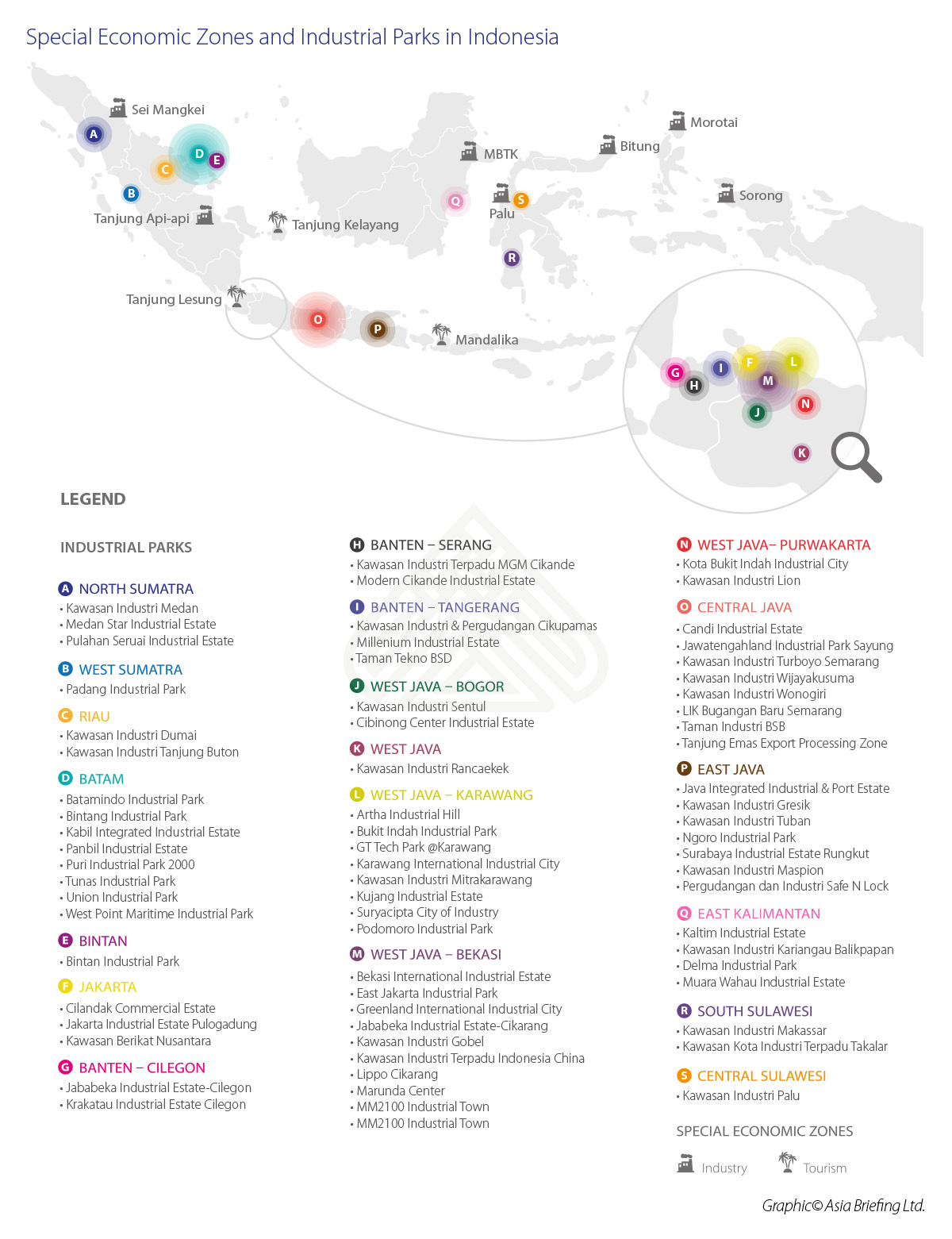
Indonesia’s Growing Special Economic Zones – Opportunities and Challenges – Zones

Over the last decade, Indonesia’s economic clusters –special economic zones (SEZs) and industrial estates have grown multi-fold, both in terms of number and breadth. In 2014, there were approximately 74 industrial estates with an area of 36,300 hectares in the country. By 2017, the number of industrial estates expanded to 87 with an area of 59,700 hectares. Similarly, the number of SEZs in the country has increased to 12; out of these, four are currently operational, representing economic activities across various industrial sectors.
Given Indonesia’s locational advantages– rich natural resources and a climate conducive to many forms of agriculture -, these clusters offer growing opportunities for investment in manufacturing, agriculture, marine, infrastructure, and tourism industries. Moreover, Indonesia has large forests areas, deposits of coal, tin, bauxite, copper, nickel, and other minerals. The country also boasts a significant oil and gas sector and is one of the leading suppliers of natural rubber.
To facilitate investment in these zones, the government of Indonesia has instituted a number of incentives targeting investors setting up within SEZs and industrial parks.
Special Economic Zones (Kawasan Ekonomi Khusus or KEKs)
The SEZs in Indonesia are open to foreign investment and offer investors access to preferential regulatory infrastructure and taxation in an attempt to channel investment into specific locations. Some of the industrial SEZs are discussed below.
Industrial SEZs in Indonesia
- SEZ Sei Mangkei
The main industries set up in Sei Mangkei include palm oil and rubber industry. Besides, there are ancillary industries established in the region such as logistic, energy, electronics, and tourism. The main products manufactured here are fatty acid, fatty alcohol, surfactant, biodiesel, and biogas.
- SEZ Tanjung Api-Api
The SEZ is a downstream industrial center of the resource-based sectors such as seed rubber, palm oil, and coal and has a good potential of water supply from the nearby Banyuasin and Telang River. It is strategically located near the Indonesian archipelago Lanes (ALKI 1) and the Strait of Malacca.
- SEZ Maloy Batuta Trans Kalimantan (MBTK)
The MBTK SEZ is located in East Kutai Regency, East Kalimantan province and consists of industrial zones, logistics, and export processing. The region is rich in natural resources such as oil palm, oil, gas, minerals, and coal. The SEZ can serve as the processing center of palm oil and its derivatives, industrial minerals, gas, coal, tourism.
- SEZ Palu
Palu provides a strategic location for the development of natural resources- based industries. These include agriculture and plantations of rubber, cocoa, rattan, seagrass, as well as the mining of nickel, gold, iron ore, and lead.
- SEZ Bitung
Located in Sulawesi Utara District, SEZ Bitung is built on an area of 534 Ha and is strategically located with international access to East Asia and the Pacific. The key industries include fisheries, oil industry, and other logistical support.
- SEZ Morotai
The Morotai Island has a famous World War II airport – Leo Wattimena Airport that has a huge runway capacity. The airport has a potential to serve as supporting infrastructure in the SEZ and increase East Indonesia’s access to the international market. The island is nestled between Asia and Australia and has short flights from Singapore and Taipei.
- SEZ Sorong
Located in Mayamuk District, KEK Sorong is built on an area of 523.7 Ha on the international trade trajectory of the Asia Pacific and Australia.
The SEZ provides several geo-economic advantages, namely potential in the fishery and marine transportation sectors. The location is also very strategic for the development of the logistics industry, agro-industry, mining, and shipyard industry.
This text is part of a more complete analysis available for free.
Read the full article on ASEAN Briefing.